2025
Multi-Strategy Named Entity Recognition System for Ancient Chinese
Wenxuan Dong, Meiling Liu# (# corresponding author)
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Ancient Language Processing (ALP) 2025 ALP2025
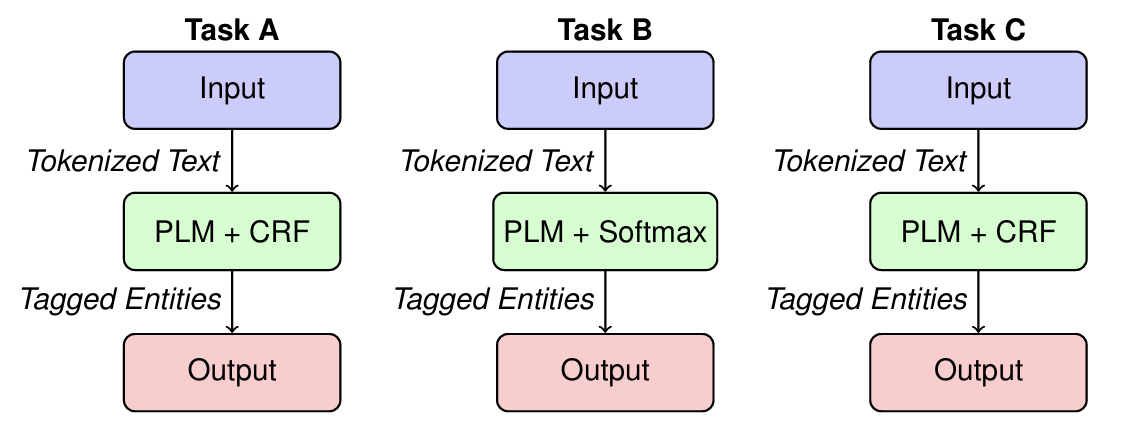
We present a multi-strategy Named Entity Recognition (NER) system for ancient Chi-nese texts in EvaHan2025. Addressing dataset heterogeneity, we use a Conditional Random Field (CRF) for Tasks A and C to handle six entity types’ complex dependencies, and a lightweight Softmax classifier for Task B’s simpler three-entity tagset. Ablation studies on training data confirm CRF’s superiority in capturing sequence dependencies and Softmax’s computational advantage for simpler tasks. On blind tests, our system achieves F1-scores of 83.94%, 88.31%, and 82.15% for Test A, B, and C—outperforming baselines by 2.46%, 0.81%, and 9.75%. With an overall F1 improvement of 4.30%, it excels across historical and medical domains. This adaptability enhances knowledge extraction from ancient texts, offering a scalable NER framework for low-resource, complex languages.
Multi-Strategy Named Entity Recognition System for Ancient Chinese
Wenxuan Dong, Meiling Liu# (# corresponding author)
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Ancient Language Processing (ALP) 2025 ALP2025
We present a multi-strategy Named Entity Recognition (NER) system for ancient Chi-nese texts in EvaHan2025. Addressing dataset heterogeneity, we use a Conditional Random Field (CRF) for Tasks A and C to handle six entity types’ complex dependencies, and a lightweight Softmax classifier for Task B’s simpler three-entity tagset. Ablation studies on training data confirm CRF’s superiority in capturing sequence dependencies and Softmax’s computational advantage for simpler tasks. On blind tests, our system achieves F1-scores of 83.94%, 88.31%, and 82.15% for Test A, B, and C—outperforming baselines by 2.46%, 0.81%, and 9.75%. With an overall F1 improvement of 4.30%, it excels across historical and medical domains. This adaptability enhances knowledge extraction from ancient texts, offering a scalable NER framework for low-resource, complex languages.