
 B.Eng., Northeast Forestry University (2025)
B.Eng., Northeast Forestry University (2025)I am an incoming master student at the ShanghaiTech University. Prior to that, I received my Bachelor's degree in computer science at Northeast Forestry University.
My research interests include Large Language Models, AI Agent and AI for Computational Lithography.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 ShanghaiTech UniversitySchool of Information Science and Technology
ShanghaiTech UniversitySchool of Information Science and Technology
M.S. StudentSep. 2025 - present -
 Northeast Forestry UniversityB.Eng. in Computer ScienceSep. 2021 - Jun. 2025
Northeast Forestry UniversityB.Eng. in Computer ScienceSep. 2021 - Jun. 2025
Honors & Awards
-
Outstanding Graduation Thesis (Top 3%), Northeast Forestry University2025
-
Third Prize in CCPC Provincial Competition2023
-
Second Prize in Blue Bridge Cup Provincial Competition (C++ Group A)2023
-
Third Prize in Group Programming Ladder Tournament (Team)2023
-
Silver Medal in Baidu Star Provincial Competition2023
-
University scholarship, Northeast Forestry University2023, 2022
News
Selected Publications (view all )
Multi-Strategy Named Entity Recognition System for Ancient Chinese
Wenxuan Dong, Meiling Liu# (# corresponding author)
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Ancient Language Processing (ALP) 2025 ALP2025
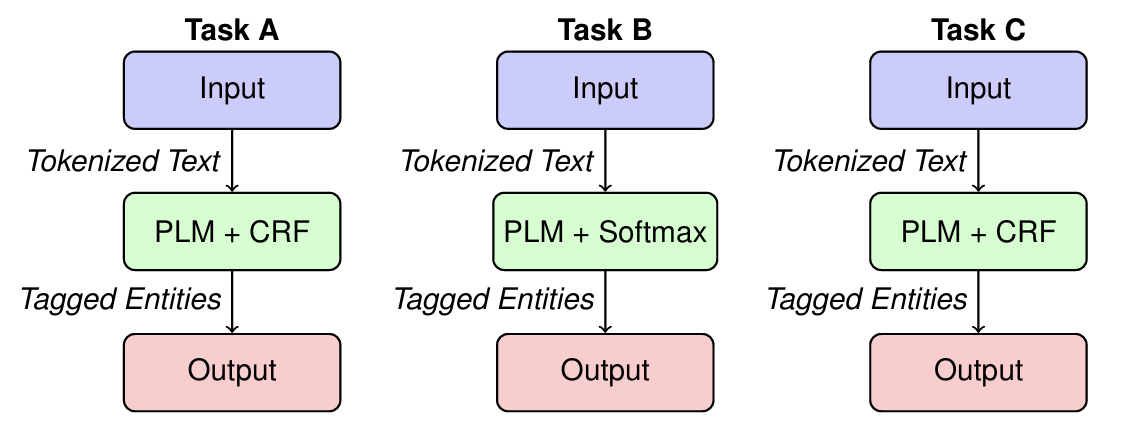
We present a multi-strategy Named Entity Recognition (NER) system for ancient Chi-nese texts in EvaHan2025. Addressing dataset heterogeneity, we use a Conditional Random Field (CRF) for Tasks A and C to handle six entity types’ complex dependencies, and a lightweight Softmax classifier for Task B’s simpler three-entity tagset. Ablation studies on training data confirm CRF’s superiority in capturing sequence dependencies and Softmax’s computational advantage for simpler tasks. On blind tests, our system achieves F1-scores of 83.94%, 88.31%, and 82.15% for Test A, B, and C—outperforming baselines by 2.46%, 0.81%, and 9.75%. With an overall F1 improvement of 4.30%, it excels across historical and medical domains. This adaptability enhances knowledge extraction from ancient texts, offering a scalable NER framework for low-resource, complex languages.
Multi-Strategy Named Entity Recognition System for Ancient Chinese
Wenxuan Dong, Meiling Liu# (# corresponding author)
Proceedings of the Second Workshop on Ancient Language Processing (ALP) 2025 ALP2025
We present a multi-strategy Named Entity Recognition (NER) system for ancient Chi-nese texts in EvaHan2025. Addressing dataset heterogeneity, we use a Conditional Random Field (CRF) for Tasks A and C to handle six entity types’ complex dependencies, and a lightweight Softmax classifier for Task B’s simpler three-entity tagset. Ablation studies on training data confirm CRF’s superiority in capturing sequence dependencies and Softmax’s computational advantage for simpler tasks. On blind tests, our system achieves F1-scores of 83.94%, 88.31%, and 82.15% for Test A, B, and C—outperforming baselines by 2.46%, 0.81%, and 9.75%. With an overall F1 improvement of 4.30%, it excels across historical and medical domains. This adaptability enhances knowledge extraction from ancient texts, offering a scalable NER framework for low-resource, complex languages.